Abscess
What is an Abscess and its Treatments?
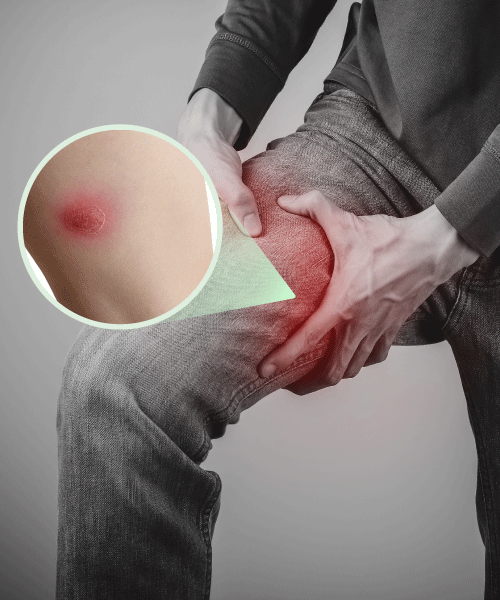
An abscess is a pocket of pus collected in the body’s tissue. Abscesses can occur anywhere in the body. Signs and symptoms of an abscess include redness, swelling, pain, and warmth at the site of the abscess. If the abscess is large enough, it may also cause fever and chills.
Abscesses in the skin may occur as cutaneous (under the skin) abscesses and are very commonly found. However, they can also occur in other tissues throughout the body, including the liver, brain, and lungs. Abscesses are caused by a build-up of pus in an enclosed space. This can happen when bacteria or other foreign material enters the body through a cut or break in the skin. The body’s immune system then works to surround and isolate the infection.
Examples are the armpit abscess, which may arise from a common condition known as Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Breast abscesses may occur in breastfeeding individuals. An anorectal abscess occurs under the skin around the anus or rectum. A pilonidal abscess occurs in the skin in the crease of the buttocks.
Signs and Symptoms
There will be redness, and an elevated or raised bump if the abscess is superficial. It may be tender to the touch, warm, or have a raised temperature. There may even be a sinus opening through which pus or inflammatory fluid may drain.
There is pain that may be well located at the site of the abscess or even spread across the surrounding areas. Fever and chills, fatigue, and weight loss all indicate abscess.
Diagnosis and tests
An abscess that is superficially located can be physically examined and treated. Deep abscess or internal abscess without external communication is diagnosed using ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI.
Treatment
Medical treatment involves the use of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. In some cases, topical application may also be necessary.
Surgical intervention
Treatment of all abscesses invariably needs drainage via a procedure. Post-procedure patients are prescribed appropriate antibiotics.
